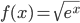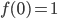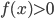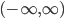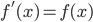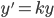You should be able to:
- Explain what is meant by an antiderivative of the function
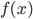 . (Section 6.1)
. (Section 6.1) - Compute all possible antiderivatives for a given function (Section 6.1)
- Compute a particular antiderivative F(x) given F(a) = b. (Section 6.1, see problems 41-47)
- Explain what is the indefinite integral of given function
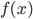 (Section 6.1)
(Section 6.1)
- Properties of the indefinite integral:
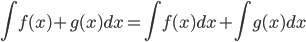 (Section 6.1)
(Section 6.1)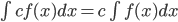
- Properties of the indefinite integral:
- Compute the indefinite integral of various functions including (this is not an exhaustive list):
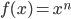 , where
, where 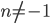
- exponential functions of the form
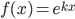
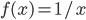
- Compute a definite integral using substitution (Section 9.1)
- You should be able to compute the definite integral for various functions. (Section 6.1)
- You should know how interpret displacement in the context of a definite integral (Section 6.2, see example 6 and problem 31 and 33)
- Explain the geometric interpretation of the definite integral
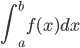 when
when 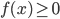 . (Answer: The area under the graph of
. (Answer: The area under the graph of 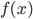 .) (Section 6.3)
.) (Section 6.3) - Compute the Riemann Sum of a function in order to approximate the area under the graph of a function. (Section 6.3)
- Using left endpoints
- Using right endpoints
- Compute area of the region bounded between the graph of a function
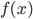 and the
and the  -axis. (Section 6.4)
-axis. (Section 6.4)